7 Signs Your Practice Needs Outsourced Revenue Cycle Management
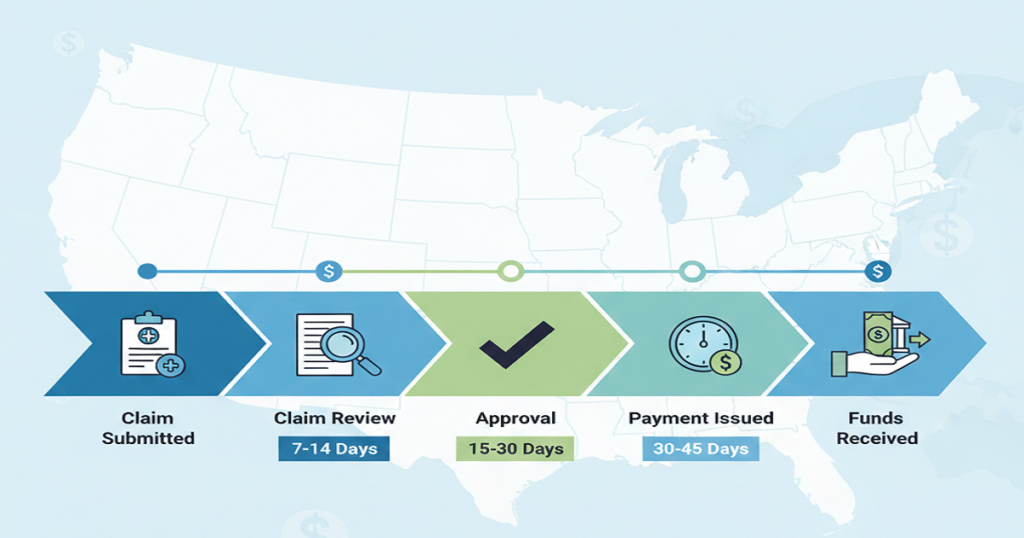
Medical BillingIf your practice stays busy but revenue feels tight, something isn’t lining up. Full schedules should translate into steady collections. When they don’t, billing usually sits at the center of the problem. Many healthcare owners wait too long to address revenue cycle issues. They assume a few denials or delayed payments are normal. However, when patterns repeat every month, the issue runs deeper. That’s where outsourced revenue cycle management becomes a smart move. Instead of stretching your internal team thin, you bring in specialists who focus only on billing performance, collections, and compliance. Let’s walk through the clear signs that it may be time to make that shift. What Is Outsourced Revenue Cycle Management? Outsourced revenue cycle management means partnering with a company that handles your billing process from start to finish. This includes insurance verification, medical coding, claim submission, denial management, accounts receivable follow-ups, patient billing, credentialing, and detailed reporting. In simple terms, it means experienced professionals manage the financial side of your practice so you can focus on patient care and growth. Now let’s look at the signs. 1. Your Claim Denial Rate Is Increasing A few denials happen in every practice. But when you start seeing that number climb, it’s time to take a closer look at your system. Things like repeated coding mistakes, missing modifiers, eligibility problems, or incomplete documentation all slow you down. Each denial means rework, which eats up time and money. An outsourced revenue cycle management team tracks denial categories by payer. They keep an eye on which payers are denying claims and why, then tackle the root issues. They clean up errors before you even submit a claim, so your first-pass acceptance rate goes up. If denials start to feel normal in your workflow, it’s time to make a change. That’s not just business as usual; it’s a warning sign. 2. Accounts Receivable Days Are Too High Look at your AR aging report. If you see big balances sitting unpaid for 60 or 90 days, that’s a problem. When payments come in late, it affects everything. Payroll becomes stressful. Vendor payments get delayed. Daily operations feel tighter than they should. Yes, you might receive that money eventually. But waiting that long still puts serious strain on your cash flow. That’s where outsourced revenue cycle management teams step in. They don’t let things slide. They’re in contact with payers, chasing down claims, fixing problems fast, and stopping old accounts from turning into write-offs. When you cut down your AR days, your monthly revenue stops swinging so much and starts feeling a lot more predictable. 3. Your Billing Team Feels Overworked Billing has become more complex over the years. Payer policies shift often. Coding updates happen regularly. Documentation standards continue to tighten. If your internal team struggles to keep up, performance naturally declines. Mistakes increase. Staff burnout rises. When someone leaves, everything slows down. Outsourcing revenue cycle management gives you access to a structured team. Coders focus on accuracy. AR specialists follow up on claims. Denial experts handle appeals. Instead of depending on one or two people, you rely on a full support system. 4. You Lack Clear Financial Reporting Strong financial performance starts with visibility. Do you know your clean claim rate? Your net collection percentage? Which insurance companies deny the most claims? If you don’t have these numbers readily available, you can’t fix weak areas effectively. Leadership needs clear data to make smart decisions. Outsourced revenue cycle management providers deliver organized performance reports. You see trends in denials, collections, AR days, and payer behavior. Clear reporting turns uncertainty into measurable action. 5. Compliance Concerns Keep Growing Coding errors don’t just slow payments. They increase audit risk. CPT codes update every year. Payer documentation rules change often. If your team misses updates, claims get rejected or flagged. An experienced outsourced revenue cycle management company keeps up with the latest coding rules and new regulations. They double-check claims before sending them out and keep a close eye on compliance. That kind of hands-on work protects your revenue and lowers your legal risk. 6. Patient Collections Are Inconsistent These days, patients are stuck paying higher deductibles and more out-of-pocket expenses. If you don’t verify insurance or collect co-pays right away, you just end up losing money. Front-end mistakes tend to cause back-end errors. Rejection occurs due to mistakes in eligibility. Patients are frustrated by confusing statements. Balances remain in longer than required. Outsourced revenue cycle management enhances both extremes. Teams ensure and maintain insurance appropriately, handle previous approvals, issue correct patient bills, and make regular follow-ups. 7. Growth Plans Feel Risky Because Revenue Isn’t Stable You can be interested in taking another provider or moving to a different place. But growth is hectic with erratic collections. Predictable revenue helps in making confident decisions. In its absence, leadership is hesitant. Outsourced revenue cycle management enhances claims accuracy, decreases denials, decreases AR cycles, and stabilizes month-to-month income. Growth becomes not a dangerous but an achievable proposition with a more robust financial framework. What Changes After You Outsource Revenue Cycle Management? Once you partner with a structured team, billing stops feeling reactive. First, claim quality improves. Clean submissions reduce rework. Next, denial management becomes organized instead of rushed. Patterns get addressed systematically. Then AR follow-ups happen consistently, which speeds up reimbursement timelines. The team follows up on unpaid claims regularly, which speeds up reimbursements. You also get straightforward reports, help with credentialing, compliance monitoring, and billing that feels organized. The entire revenue process starts to make sense. Over time, collections become more predictable. Leadership spends less time troubleshooting billing problems and more time improving services. Why Healthcare Providers Choose Rapid RCM Solutions If several of these signs apply to your practice, it may be time to strengthen your billing process. Rapid RCM Solutions provides complete outsourced revenue cycle management services for hospitals, specialty clinics, labs, and private practices across the United States. Their team handles medical billing and coding, denial management, AR follow-ups, credentialing, compliance oversight, and
7 Signs Your Practice Needs Outsourced Revenue Cycle Management Read More »